Table Of Content
Table Of Content
At present, there are mainly 1.3, 1.4, 2.0, and 2.1 versions of the HDMI market, and the 2.0 version of the cable and plug is actually the same as the 1.4 version, and the test standards are the same. So in fact, there are only two versions, 1.3 and 1.4/2.0, but 2.0 has 4K test requirements. How to quickly distinguish the cable specifications of each version of HDMI? Let’s take a look together!

HDMI function description:
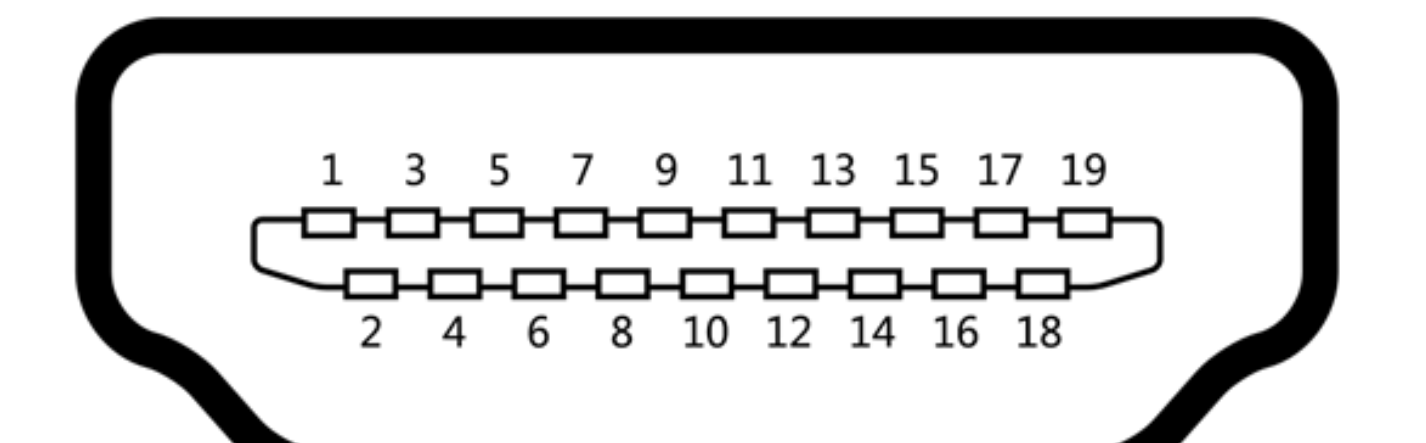
4 sets of signal lines transmit TDMS high-frequency signals (Transition Minimized Differential Signaling, differential signals), which are prone to crosstalk. In order to ensure the transmission quality, each set should be wrapped with aluminum foil to shield interference; in the 19PIN HDMI connector, 1-12PIN is connected to 4 sets of signals 7 electronic wires are soldered on 13-19PIN, 13PIN is the CEC consumer electronics function (Consumer Electronics Control), that is, one remote control can control multiple HDMI-connected devices
14PIN is a reserved point, a reserved PIN without any function

15 and 16PIN belong to DDC ((DirectDigital Control, display data channel), used to read EDID (Extended Display Identification Data) hardware information, to communicate the resolution/audio/color depth and other information output display of the playback and receiving equipment, and also carry out HDCP key (anti-piracy verification) exchanges verification information (verification every 2 seconds). DDC includes two pins, SCL (SerialClock) and SDA (SerialData), which are generally connected with orange/yellow core wires by default.
Among them, 15PIN is the DDC_SCL pin, which works together with 16PIN and is responsible for controlling the data transmission of DDC_SDA.
Among them, 16PIN is the DDC_SDA pin, which works together with 15PIN and is responsible for DDC data transmission.
17PIN is the ground wire of DDC and CEC
18PIN is a +5V power supply, which is used to supply power to the TV to read DDC information, that is, the TV can be read without plugging in the power supply.
19PIN is a hot plug function (Hot Plug Detect), used to detect whether there is a physical connection between the playback device and the display device
Compared with version 1.3, version 1.4 has the same number of core wires, and a set of signal wires is added to be responsible for the Ethernet function, that is, the electronic wires connected to the 14/19 pins of 1.3 are made into foam wires to improve the transmission effect, and then the original 17 points The electronics used as the ground wire are twisted together to wrap aluminum foil (17PIN is DDC/CEC/Ethernet three-in-one ground wire), which becomes the fifth group of signal wires, which are specially responsible for transmitting Ethernet data and audio return data (not responsible for image data , not directly related to the other 4 groups of signal pairs), 19PIN is still hot-swappable. The original 13PIN is CEC function unchanged, 15 and 16 are DDC channel functions also unchanged, 18 points are +5V power supply also unchanged.
HDMI material and function
The IDs of the above core wires are different from each factory, and there is no mandatory requirement for the ID size, just pay attention to the size of the conductor. For more specifications, please Baidu: AWG Specification Comparison Table
HDMI total stranded outer diameter = foam core diameter * 5.2, for example, 30AWG foam core diameter is 0.7, then total stranded outer diameter = 0.7 * 5.2 = 3.64mm
Braided diameter = single conductor diameter * 5 + total stranded outer diameter, for example, braided conductor is 0.12mm, braided outer diameter = 0.12*5+3.64=4.24mm (continue to the above calculation)
The difference between multi-strand and single-strand conductors:
If the conductors are used to transmit high-frequency signals, 7 conductors are required to be twisted into a perfect circle, that is, 1 in the center and 6 around. If there are 19 conductors, the third layer will add 6 more conductors than the second layer, that is, 1 +6+12. In theory, the effect of single-strand and multi-strand transmission is the same.
Advantages of multi-strand conductors: The wires made are softer than single strands, and if individual conductors are broken, they can still be used normally;
Disadvantages: more stranding process, increase cost, if stranding is not done well, strands cannot be twisted into a perfect circle when jumping strands,
It will affect the signal transmission effect, and the stability is worse than that of single strands, so usually HDMI uses 7 strands to make multiple strands, instead of 19 strands, because the more strands, the more difficult it is to twist.
In addition, for example, why 1/0.404BC and 7/0.16 are both 26AWG, because the cross-sectional area is close to the same, because AWG is integrated according to the cross-section. Multi-strand conductors should be twisted, otherwise it is difficult to process.
The larger the AWG number, the smaller the conductor. 7/0.16 can also be written as 7/34AWG, because the diameter of 34AWG is 0.16mm; the ground wire is sometimes represented by D, and sometimes by D.W, that is, Drain Wire.